Publication Date: 2025-04-10 | Regulator: BOE
Title: PRA Business Plan 2025/26
Main Objective/ Summary
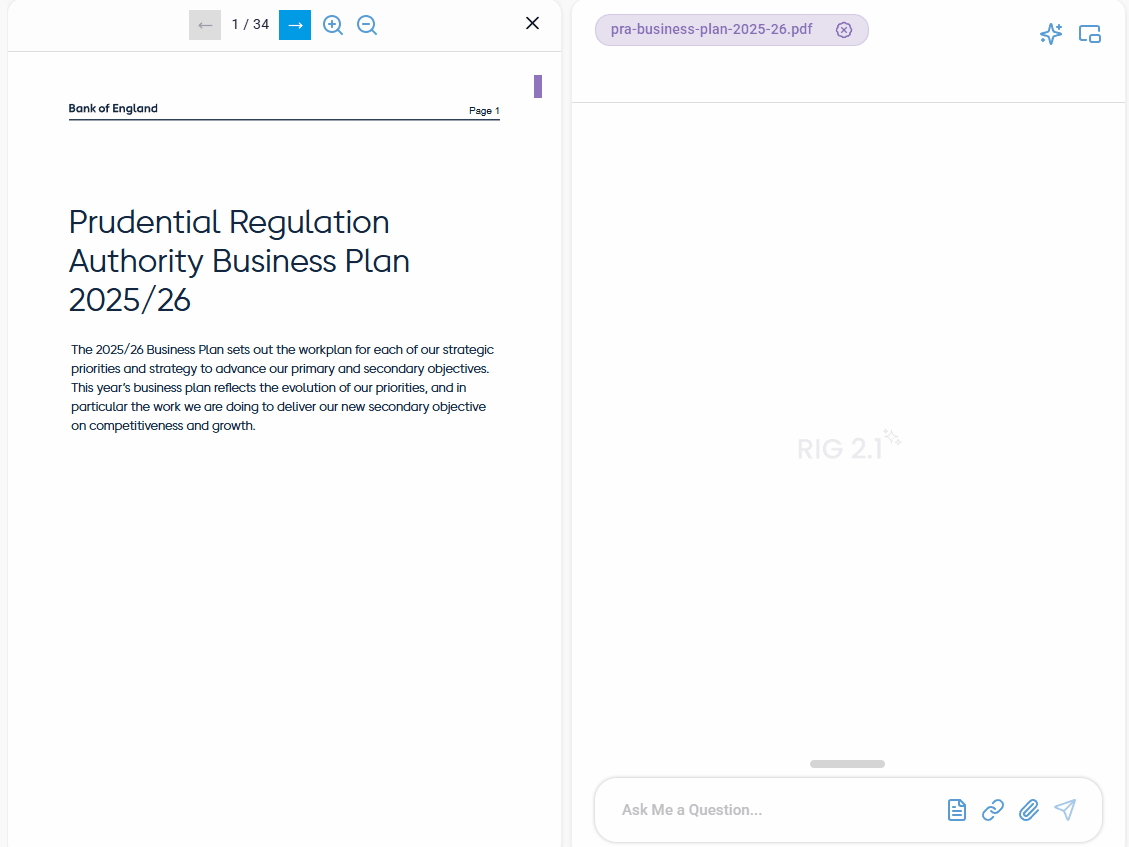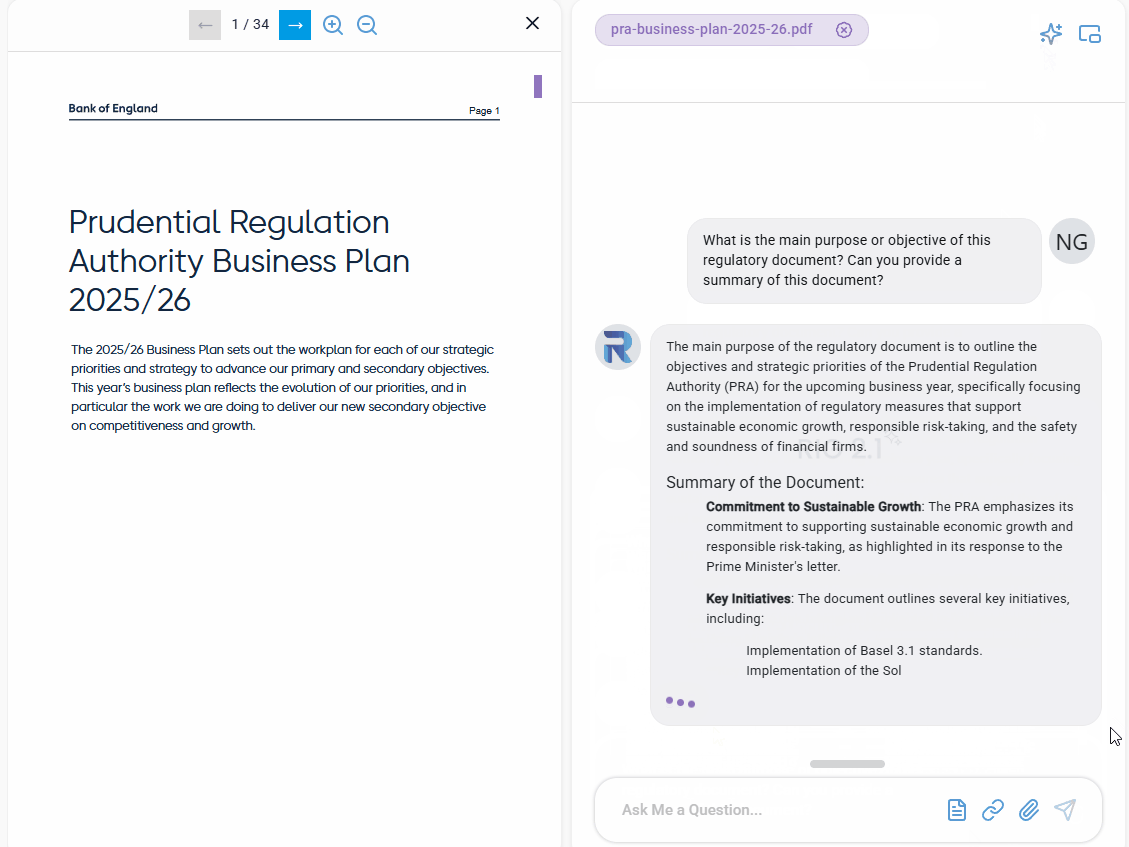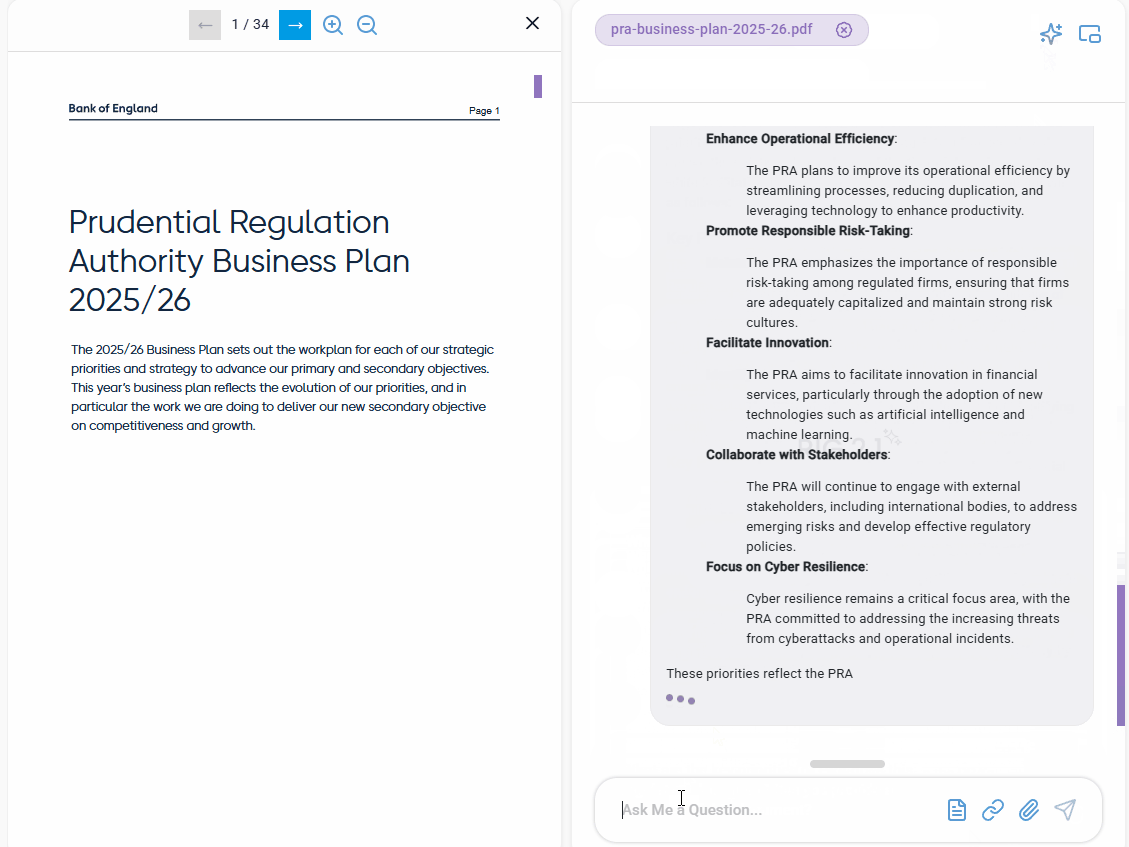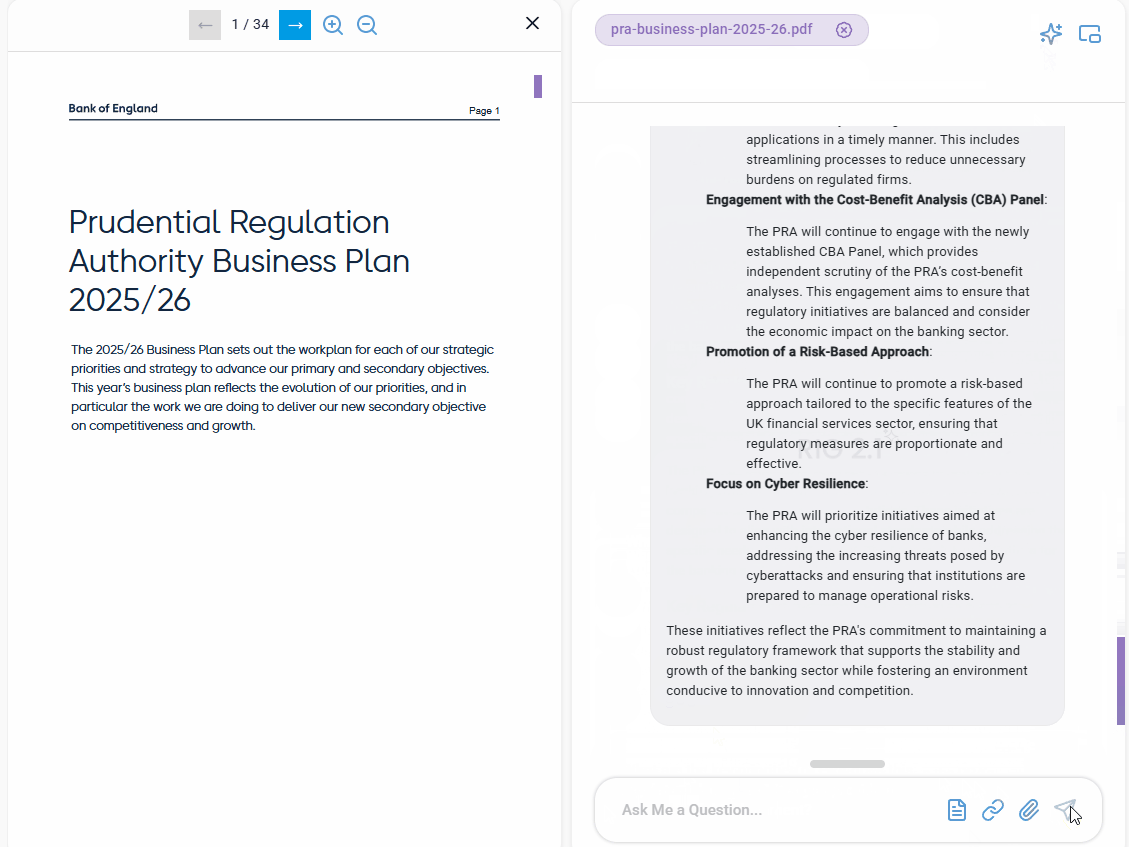
The main purpose of the regulatory document is to outline the objectives and strategic priorities of the Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) for the upcoming business year, specifically focusing on the implementation of regulatory measures that support sustainable economic growth, responsible risk-taking, and the safety and soundness of financial firms.
Summary of the Document:
- Commitment to Sustainable Growth: The PRA emphasizes its commitment to supporting sustainable economic growth and responsible risk-taking, as highlighted in its response to the Prime Minister’s letter.
- Key Initiatives: The document outlines several key initiatives, including:
- Implementation of Basel 3.1 standards.
- Implementation of the Solvency UK regime for insurers.
- Removal of the ‘bonus cap’ for banks.
- Review of the Senior Managers and Certification Regime (SM&CR) in collaboration with the FCA and HMT.
- Enhancements to the PRA’s operational efficiency.
- Regulatory Focus: The PRA’s regulatory focus is primarily at the individual firm and sector level, with a risk-based approach to regulation and supervision. The PRA aims to be a strong, accountable, and accessible policymaker.
- Objectives: The PRA has two primary objectives:
- Promote the safety and soundness of PRA-authorized persons.
- Protect policyholders, specifically for insurance firms.
Additionally, it has two secondary objectives:
- Facilitate effective competition in the markets for services provided by PRA-authorized persons.
- Support the international competitiveness and growth of the UK economy.
- Operational Resilience: The document highlights the importance of operational and cyber resilience, with plans to conduct stress tests for both banking and life insurance sectors and to consult on policies related to Information and Communication Technology (ICT) management.
- Efficiency and Productivity: The PRA aims to maintain efficiency in its processes, particularly regarding the timeliness of authorization applications, while managing costs effectively.
- Collaboration with Other Authorities: The PRA works closely with the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and other committees within the Bank of England to ensure a cohesive regulatory approach.
This document serves as a strategic framework for the PRA’s regulatory activities and priorities for the upcoming year, reflecting its commitment to balancing safety, soundness, and growth within the financial services sector.
Key Strategic Priorities of PRA
The PRA’s strategic priorities for the 2025/26 business plan are designed to advance its primary and secondary objectives while ensuring the safety and soundness of the financial services sector. The key strategic priorities outlined in the document are as follows:
PRA’s Strategic Priorities for 2025/26:
- Maintain and Ensure the Safety and Soundness of the Banking and Insurance Sectors:
- The PRA aims to uphold the resilience of the banking and insurance sectors by ensuring that regulated firms remain adequately capitalized, maintain sufficient liquidity, and have stable funding profiles. This priority reflects the PRA’s commitment to protecting policyholders and supporting overall financial stability.
- Be at the Forefront of Identifying New and Emerging Risks:
- The PRA is focused on proactively identifying and addressing emerging risks that may affect its statutory objectives. This includes working closely with external stakeholders and international bodies to monitor trends and developments in the financial sector, particularly in relation to technological advancements and their implications.
- Support Competitive, Dynamic, and Innovative Markets:
- The PRA is committed to facilitating international competitiveness and growth within the sectors it regulates. This involves promoting an environment that supports innovation while ensuring that regulatory frameworks are conducive to dynamic market conditions.
- Run an Inclusive, Efficient, and Responsive Regulator:
- The PRA aims to enhance its operational effectiveness by fostering an inclusive culture and ensuring that its regulatory processes are efficient and responsive to the needs of regulated firms. This includes engaging with stakeholders and continuously improving its operational practices.
- Enhancing Productivity, Data, and Technology:
- The PRA is focused on improving its productivity through the adoption of new technologies and data management practices. This includes the implementation of automation in operational processes and the development of a new supervisory platform to enhance analytical capabilities.
These strategic priorities reflect the PRA’s commitment to maintaining a robust regulatory framework that supports the stability and resilience of the financial services sector while adapting to new challenges and opportunities in the evolving economic landscape.
Key Regulatory Initiatives
Banking
The PRA has outlined several key regulatory initiatives for the banking sector aimed at enhancing the safety, soundness, and competitiveness of financial institutions. These initiatives are designed to align with international standards while addressing the specific needs of the UK market. The key regulatory initiatives for the banking sector include:
Key Regulatory Initiatives for the Banking Sector:
- Implementation of Basel 3.1 Standards:
- The PRA is finalizing its policy and rules for the remaining parts of the Basel III standards, known as the Basel 3.1 standards. This includes tailoring international rules to better suit the UK market and making adjustments based on industry feedback to enhance competitiveness and growth.
- Lowering Capital Requirements:
- As part of the Basel 3.1 implementation, the PRA has made significant changes to lower capital requirements to support lending to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), infrastructure projects, and trade finance. This aims to stimulate economic growth while ensuring the overall capital requirements for the UK banking system remain stable.
- Review of the Senior Managers and Certification Regime (SM&CR):
- The PRA, in collaboration with the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and Her Majesty’s Treasury (HMT), will review the SM&CR to ensure it remains effective in promoting accountability and good governance within banks.
- Enhancing Operational Effectiveness:
- The PRA is focused on improving its operational effectiveness by handling authorization applications in a timely manner. This includes streamlining processes to reduce unnecessary burdens on regulated firms.
- Engagement with the Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) Panel:
- The PRA will continue to engage with the newly established CBA Panel, which provides independent scrutiny of the PRA’s cost-benefit analyses. This engagement aims to ensure that regulatory initiatives are balanced and consider the economic impact on the banking sector.
- Promotion of a Risk-Based Approach:
- The PRA will continue to promote a risk-based approach tailored to the specific features of the UK financial services sector, ensuring that regulatory measures are proportionate and effective.
- Focus on Cyber Resilience:
- The PRA will prioritize initiatives aimed at enhancing the cyber resilience of banks, addressing the increasing threats posed by cyberattacks and ensuring that institutions are prepared to manage operational risks.
These initiatives reflect the PRA’s commitment to maintaining a robust regulatory framework that supports the stability and growth of the banking sector while fostering an environment conducive to innovation and competition.
Insurance Sector
The PRA has identified several key regulatory initiatives for the insurance sector aimed at enhancing its resilience, promoting investment, and ensuring effective regulation. These initiatives are designed to align with the PRA’s objectives of safety and soundness while facilitating innovation and growth within the insurance industry. The key regulatory initiatives for the insurance sector include:
Key Regulatory Initiatives for the Insurance Sector:
- Implementation of Solvency UK:
- The PRA has implemented the new Solvency UK prudential regime for insurers, which includes significant changes to the capital regime. This reform aims to enable the life insurance sector to play a larger role in investing in the UK economy across a broader range of assets.
- Reform of Matching Adjustment Rules:
- As part of the Solvency UK implementation, the PRA has reformed the Matching Adjustment (MA) rules to align with the legislative framework set by the Government. This reform is intended to enhance the ability of insurers to invest in long-term assets, thereby supporting economic growth.
- Establishment of a Matching Adjustment Application Process:
- The PRA has established a new MA application process and a dedicated MA permissions team to improve the speed and efficiency of processing new MA applications, particularly those involving newly eligible assets.
- Development of the Matching Adjustment Investment Accelerator:
- The PRA is consulting on the establishment of a Matching Adjustment Investment Accelerator, which aims to further reduce barriers to investment by insurance firms. This initiative is designed to enable insurers to deliver on their commitments to make additional investments in the UK economy more quickly.
- Collaboration with HMT and the National Wealth Fund (NWF):
- The PRA is engaging in discussions with HMT, the NWF, and the insurance industry to unlock new opportunities for productive investment by insurers in sectors targeted by the NWF.
- Focus on Operational Effectiveness:
- The PRA is committed to improving its operational effectiveness by ensuring timely handling of authorization applications and enhancing the overall efficiency of its regulatory processes.
- Embedding the Secondary Competitiveness and Growth Objective (SCGO):
- The PRA is working to embed the SCGO into its policymaking processes and supervisory approach, ensuring that competitiveness and growth considerations are integrated into regulatory decisions.
- Engagement with Stakeholders:
- The PRA will continue to engage with industry stakeholders to gather feedback and improve its regulatory framework, ensuring that it remains responsive to the needs of the insurance sector.
These initiatives reflect the PRA’s commitment to fostering a robust and resilient insurance sector that can effectively contribute to the UK economy while maintaining high standards of regulatory oversight.
Multi Sector
The PRA has outlined several key regulatory initiatives that span multiple sectors, focusing on enhancing the overall effectiveness of regulation, promoting competitiveness, and ensuring the safety and soundness of financial institutions. The multi-sector initiatives are designed to address common challenges and opportunities across the banking and insurance sectors. The key regulatory initiatives for the multi-sector include:
Key Multi-Sector Regulatory Initiatives:
- Embedding the Secondary Competitiveness and Growth Objective (SCGO):
- The PRA is actively working to integrate the SCGO into its regulatory framework and decision-making processes. This involves ensuring that considerations of competitiveness and growth are factored into regulatory initiatives across all sectors.
- Streamlining Regulatory Processes:
- The PRA aims to improve the efficiency of its regulatory operations by streamlining processes and reducing unnecessary burdens on regulated firms. This includes enhancing the speed and effectiveness of regulatory transactions.
- Enhancing Operational Effectiveness:
- The PRA is focused on improving its operational effectiveness across sectors, including timely handling of authorization applications and ensuring that regulatory measures are proportionate and effective.
- Engagement with Industry Stakeholders:
- The PRA will continue to engage proactively with firms and other relevant stakeholders through industry roundtables and feedback mechanisms. This engagement is intended to improve interactions and adapt to changes in the operating environment.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) Framework:
- The PRA is committed to enhancing its CBA framework to ensure that regulatory initiatives are balanced and consider the economic impact on the sectors it regulates. This includes ongoing engagement with the CBA Panel for independent scrutiny.
- Focus on Technology and Innovation:
- The PRA is dedicated to fostering innovation and the adoption of new technologies across sectors. This includes initiatives aimed at improving data and technology capabilities to enhance regulatory effectiveness.
- Proactive Risk Management:
- The PRA will continue to identify and address emerging risks that may impact multiple sectors, ensuring that regulatory measures are in place to mitigate these risks effectively.
- Collaboration with Other Regulatory Bodies:
- The PRA will work closely with other regulatory bodies, such as the FCA and HMT, to ensure a coordinated approach to regulation that supports the overall stability and growth of the financial services sector.
These multi-sector initiatives reflect the PRA’s commitment to maintaining a robust regulatory framework that supports the resilience and competitiveness of the financial services industry while addressing the unique challenges faced by different sectors.
Operational effectiveness
The PRA has outlined several key regulatory initiatives aimed at enhancing operational effectiveness within the financial services sector. These initiatives are designed to ensure that the PRA can effectively oversee regulated firms while adapting to new risks and opportunities. Below are the primary initiatives highlighted in the document:
Key Regulatory Initiatives for Operational Effectiveness:
- Streamlining Authorisation Processes:
- The PRA aims to improve the efficiency of its authorisation processes, which include handling over 1,800 regulatory transactions annually. The focus is on maintaining high levels of operational effectiveness while ensuring that authorisation decisions are made in a timely manner. The PRA has reported that 99.7% of statutory cases were handled within deadlines in 2024.
- Enhancing Technology and Data Capabilities:
- The PRA is investing in technology and data capabilities to support its operational effectiveness. This includes the design of a new supervisory platform that will provide staff with access to advanced tools and training opportunities, enabling them to work more efficiently and effectively.
- Automation of Operational Processes:
- The PRA is implementing initiatives to remove duplication in operational processes and increase the use of automation for repeatable tasks. This is expected to enhance productivity and reduce inefficiencies in supervision, authorisation, and policymaking.
- Proactive Engagement with Firms:
- The PRA is committed to fostering proactive engagement with regulated firms and stakeholders. This includes using industry roundtables and feedback from annual firm surveys to improve interactions and adapt to changes in the operating environment.
- Continuous Improvement of Risk Controls:
- The PRA is focused on maintaining strong risk controls while streamlining regulatory transactions. This involves ongoing assessments of risk management practices and ensuring that firms adhere to regulatory expectations.
- Support for International Firms:
- The PRA is working to deliver a ‘concierge service’ to assist international firms in navigating the UK regulatory landscape when considering establishing new businesses. This initiative aims to facilitate smoother interactions and support international competitiveness.
- Monitoring and Reporting Metrics:
- The PRA publishes quarterly metrics on the timeliness of authorisation decisions, which helps to maintain transparency and accountability in its operations. This practice supports continuous improvement and operational effectiveness.
- Embedding the Secondary Competitiveness and Growth Objective (SCGO):
- The PRA is embedding the SCGO into its processes to promote sustainable economic growth and responsible risk-taking. This includes developing initiatives that advance competitiveness and growth in the banking and insurance sectors.
- Engagement with the Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) Panel:
- The PRA has established a CBA Panel to provide independent scrutiny of its cost-benefit analyses. This engagement is intended to enhance the PRA’s decision-making processes and ensure that regulatory initiatives are effective and proportionate.
- Focus on Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI):
- The PRA recognizes the importance of DEI in enhancing operational effectiveness. Initiatives aimed at promoting an inclusive culture and diverse workforce are expected to contribute to better decision-making and overall effectiveness.
By implementing these key regulatory initiatives, the PRA aims to enhance its operational effectiveness, improve its responsiveness to emerging risks, and ensure that it can effectively oversee the firms it regulates while supporting the stability of the UK financial system.
Key Implementation Dates and Transitional Periods
The document outlines several key implementation dates and transitional periods relevant to regulatory changes and initiatives within the financial services sector. Below is a summary of these important dates and periods:
Key Implementation Dates and Transitional Periods:
- Basel 3.1 Standards:
- Implementation Date: The implementation date for the Basel 3.1 standards has been delayed to 1 January 2027. This delay allows for greater clarity around plans for implementation in the US.
- Transitional Arrangements: The transitional arrangements in the rules will be reduced to 3 years, ensuring that full implementation remains targeted for 1 January 2030.
- Strong and Simple Framework for Small Domestic Deposit Takers (SDDTs):
- The PRA published proposals for a simplified capital regime and additional liquidity simplifications for SDDTs in September 2024.
- The PRA intends to publish a policy statement on the simplified capital regime in Q4 2025 and will implement the simplified capital regime thereafter.
- Bank Capital Stress Test:
- The PRA and the Bank will conduct a Bank Capital Stress Test in 2025, which will involve the largest and most systemic UK banks. This test will be carried out every other year.
- Securitisation Rules:
- The PRA intends to consult on further changes to the securitisation rules in H2 2025 to make the existing framework more proportionate.
- Finalisation of PRA Rules:
- The PRA intends to publish its final rules regarding the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR) once Parliament has revoked the relevant parts of the CRR.
These key dates and transitional periods are critical for regulated firms to prepare for upcoming regulatory changes and ensure compliance with the evolving regulatory landscape.
Amendments to Existing Regulations
The document outlines several amendments to existing regulations introduced by the PRA. These amendments are primarily aimed at enhancing competitiveness, streamlining regulatory processes, and aligning with international standards. Below are the key amendments highlighted in the document:
Key Amendments to Existing Regulations:
- Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR):
- The PRA has prioritized the CRR as a focus area in the process of transferring assimilated law into the supervisory authorities’ rules and legislation following the enactment of the Financial Services and Markets Act (FSMA) 2023. The PRA intends to replace assimilated law with PRA rules, with modifications where appropriate, to better suit the UK market.
- Implementation of Basel 3.1 Standards:
- The PRA has made significant adjustments to the capital requirements as part of the implementation of the Basel 3.1 standards. These adjustments include lowering capital requirements to support lending to SMEs, infrastructure projects, and trade finance, while ensuring that overall capital requirements for the UK banking system do not significantly increase.
- Amendments to Remuneration Requirements:
- The PRA is consulting on amendments to remuneration requirements for banks, specifically reducing the period for which bonuses must be deferred. This change aims to enhance competitiveness within the banking sector.
- Securitisation Regulation Changes:
- The PRA has proposed substantive policy changes to the securitisation framework, including modifications to the standardised approach and the capital treatment of residential mortgages under the Government’s mortgage guarantee scheme. These changes are part of the PRA’s efforts to make the existing securitisation rules more proportionate.
- Streamlining Regulatory Data Reporting:
- The PRA plans to consult on initial proposals to simplify regulatory data reporting for banks, following previous steps taken to reduce reporting requirements for insurers. This initiative aims to alleviate the reporting burden on firms while maintaining effective oversight.
- Matching Adjustment Investment Accelerator:
- The PRA is consulting on the introduction of a Matching Adjustment Investment Accelerator, which aims to further reduce barriers to investment by insurance firms, thereby enhancing their ability to invest in long-term assets.
These amendments reflect the PRA’s ongoing efforts to adapt the regulatory framework to better support the needs of the financial services sector while ensuring compliance with international standards and promoting competitiveness and growth.
Actions that Firms Need to Take
The document outlines several actions that firms are expected to take in response to the regulatory initiatives and amendments introduced by the PRA. These actions are aimed at enhancing compliance, improving risk management, and aligning with the evolving regulatory landscape. Below are the key actions firms are encouraged to undertake:
Actions Firms Are Expected to Take:
- Enhance Operational Resilience:
- Firms are expected to strengthen their operational resilience frameworks to ensure they can detect, withstand, and recover from ICT and cyber incidents. This includes developing robust contingency plans and testing their effectiveness.
- Implement Changes to the Senior Managers & Certification Regime (SM&CR):
- Firms should prepare for upcoming changes to the SM&CR, which aim to improve clarity, efficiency, and proportionality. This includes ensuring that senior managers understand their responsibilities and that firms have appropriate governance structures in place.
- Manage Climate-Related Risks:
- Firms are required to assess and manage climate-related financial risks in line with the PRA’s expectations. This includes integrating climate risk into their risk management frameworks and reporting on their progress in managing these risks.
- Adapt to Basel 3.1 Standards:
- Firms must implement the changes associated with the Basel 3.1 standards, including adjustments to capital requirements and risk management practices. This involves reviewing and updating internal policies and procedures to align with the new standards.
- Engage with Regulatory Consultations:
- Firms are encouraged to actively participate in regulatory consultations, including those related to the SM&CR and climate-related risk management. Providing feedback and insights during these consultations is essential for shaping effective regulatory outcomes.
- Review and Update Remuneration Policies:
- Firms should review their remuneration policies in light of the proposed amendments to remuneration requirements, ensuring that they remain competitive while adhering to regulatory expectations.
- Streamline Regulatory Reporting:
- Firms are expected to adapt to the PRA’s initiatives aimed at simplifying regulatory reporting requirements. This may involve updating internal reporting processes and systems to ensure compliance with new standards.
- Enhance Risk Management Frameworks:
- Firms should strengthen their risk management frameworks to address emerging risks, including those related to technology, operational resilience, and climate change. This includes conducting regular risk assessments and ensuring that risk management practices are embedded in decision-making processes.
- Promote a Strong Risk Culture:
- Firms are encouraged to foster a strong risk culture that prioritizes effective risk management and governance. This involves training staff, promoting accountability, and ensuring that risk considerations are integrated into business strategies.
- Monitor and Report on Progress:
- Firms should establish mechanisms to monitor and report on their progress in implementing the required changes and meeting regulatory expectations. This includes regular updates to senior management and the board on compliance status and risk management efforts.
By taking these actions, firms can enhance their compliance with regulatory requirements, improve their resilience to risks, and contribute to the overall stability and integrity of the UK financial system.